- Tolerance ± 0.01mm
- Low Volume Production
- 3 days Rapid Prototyping
- DFM Feedback
- Delivery within 1 Week
Injection Molding Processes
CNC machining can work with a wide range of materials, including metals (such as aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics (such as ABS, acrylic, nylon), wood, foam, composites, and even certain types of ceramics. The suitability of a material for CNC machining depends on factors such as its hardness, machinability, and thermal properties.
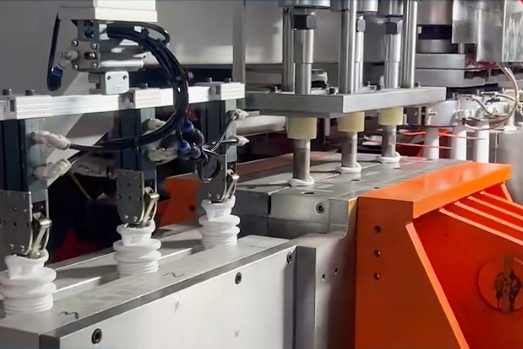
Blow Molding
Blow molding involves clamping molten thermoplastic material into a mold and blowing air into it to expand against the mold cavity walls. After cooling and solidifying, the desired product shape is formed.
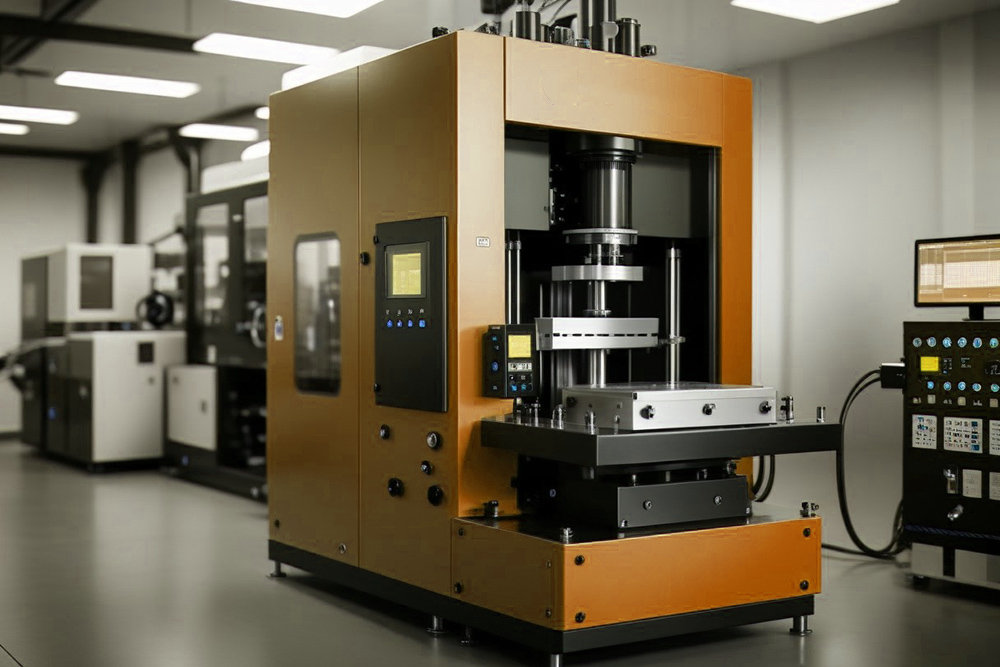

Compression Molding
Compression molding is mainly for molding thermosetting plastics and comes in two types: compression molding and transfer molding, which vary based on material characteristics and processing equipment.

Insert Molding
Insert molding refers to a molding process where a pre-prepared insert of a different material is placed into a mold, and then resin is injected. The molten material bonds and solidifies with the insert, resulting in a single integrated product.
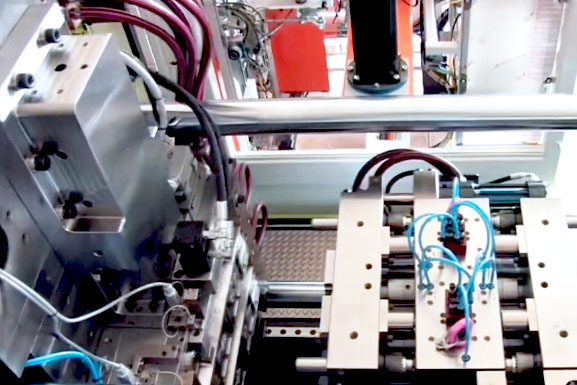
Two Shot Molding
Two-shot injection molding injects two different-colored plastics into one mold, creating distinct color effects and enhancing the part's aesthetics with patterns.
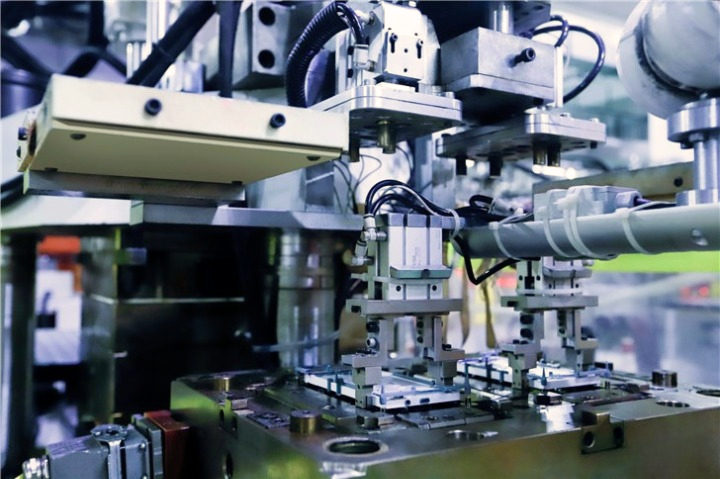

Nano Injection Molding
It is a process that combines metal and plastic using nanotechnology. The metal surface is first treated with nanotechnology, and then plastic is directly injected and molded onto the metal surface, allowing the metal and plastic to be integrated.

Overmolding
Overmolding is when reinforcement materials are encapsulated within a matrix material, enhancing the composite's properties. It improves mechanical, thermal, and electromagnetic performance, with precise control for stability.
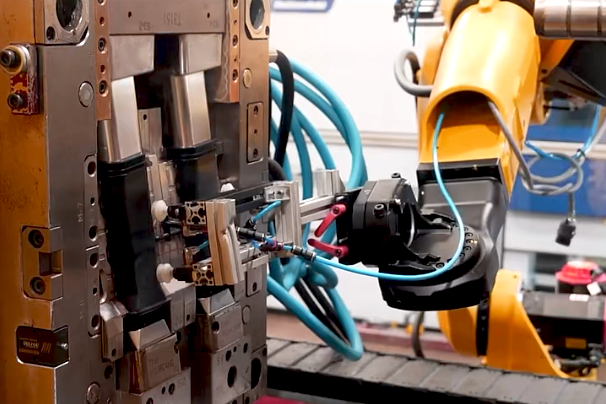
Injection Molding
Injection molding feeds granular or powdered raw material into an injection machine's hopper, where it's heated and melted. The molten material is then injected into the mold cavity through the nozzle and gating system, solidifying to form the desired shape.

Rotational Molding
Rotational molding involves adding plastic raw materials into a mold, which rotates along two perpendicular axes while being heated. This process allows the plastic to coat the entire mold surface evenly, forming the desired shape.
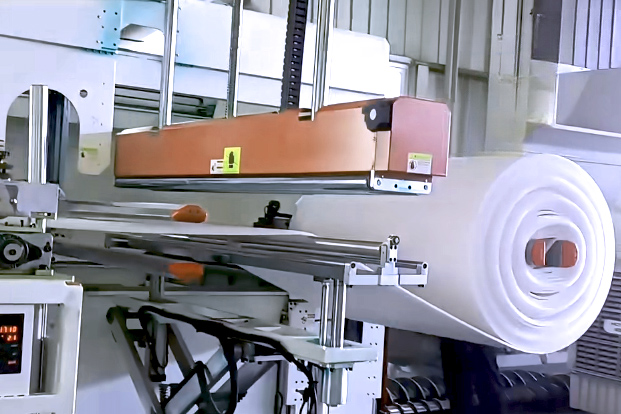

Structural Foam Molding
It is a manufacturing process that injects a gas into melted plastic resin to create lightweight, strong parts with a foamed core. It's used to produce large, thick-walled components with excellent strength and dimensional stability, commonly found in automotive and construction industries.
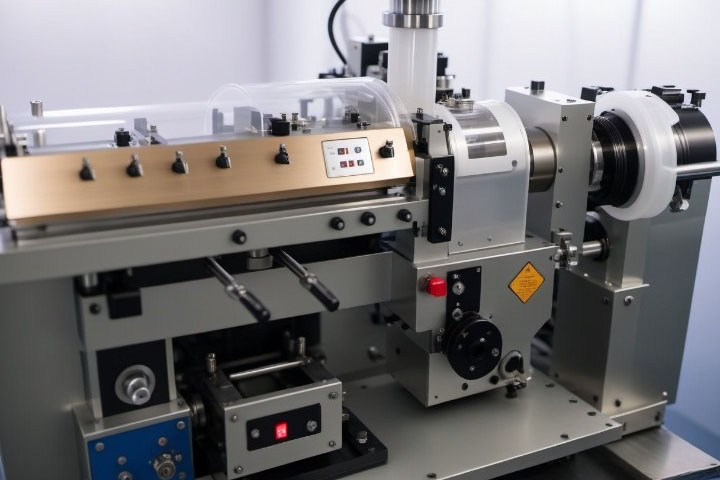

Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding is mainly used for molding thermoplastic materials. It involves melting the material and pushing it through a shaped opening using a rotating screw. After shaping, the material is cooled and hardened to produce the final product.

Dip Molding
Dip molding uses the flowability of thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions, allowing them to be shaped into desired forms through jetting and solidification at room temperature using specialized tools and methods.
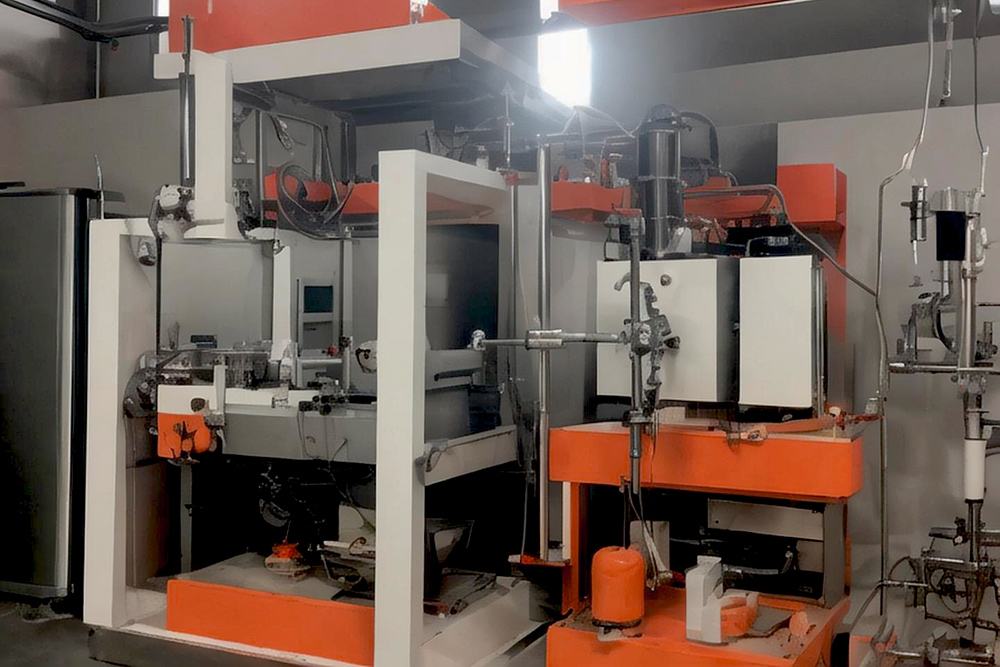

Thermoforming
Thermoforming, also known as vacuum forming, is a method where sheet materials are heated, vacuumed onto a mold, and cooled to create plastic products.
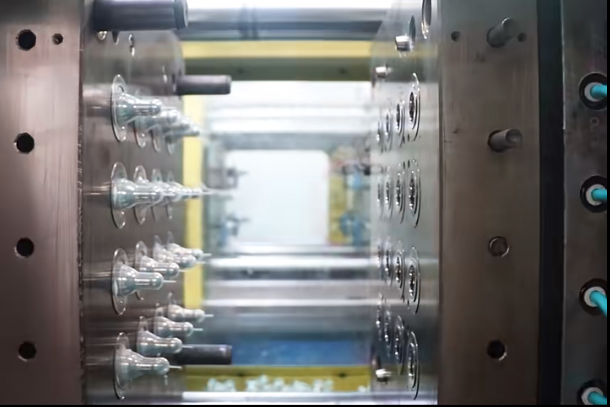
Injection Molding
Also known as injection-compression molding, utilizes the pressure of an injection molding machine to directly inject preheated rubber material from the barrel through a nozzle into the mold cavity, where it undergoes vulcanization to form the desired shape.
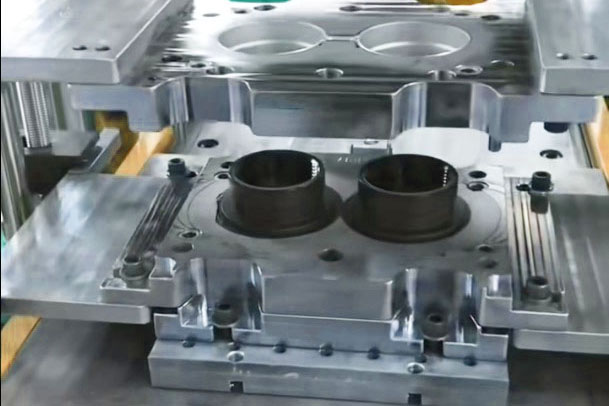

Compression Molding
Rubber compression molding places preprocessed rubber materials into an open mold cavity, which is then closed and subjected to pressure and heat in a vulcanizing press. This process causes the rubber to vulcanize and take shape.
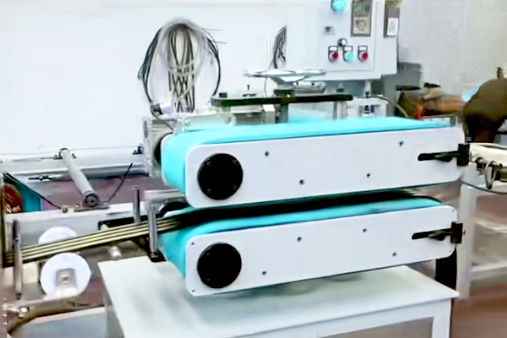
Transfer Molding
Transfer molding, also called transfer compression or potting molding, places preprocessed rubber strips or blocks into a transfer mold cavity. The rubber is compressed by the transfer plunger and forced into the mold cavity through the gating system for vulcanization and shaping.
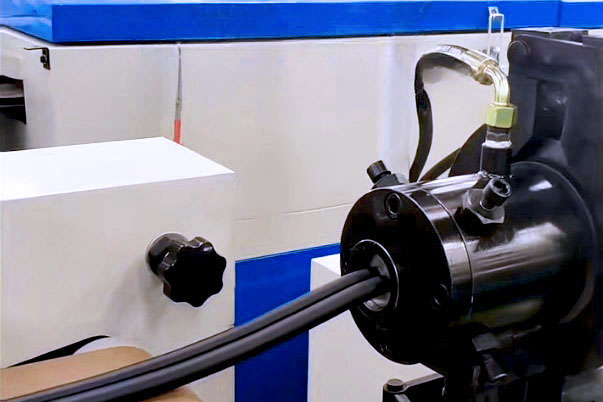
Extrusion Molding
Rubber extrusion molding heats and plasticizes rubber material in an extruder, pushing it forward with a screw or plunger. It then extrudes various semi-finished products using a rubber extrusion mold to complete the forming process.
Injection Molding Materials
When speaking to the materials for injection molding, you know ABS, PC, PE, PP, PS, PA, POM, etc. But they are much more than these, and come with different performances. In generally, they can be divided to thermoplastic polymer, thermoset polymer, and rubber.
- Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Nylon Polyamide (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polyoxymethylene (POM)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
- Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Polyethersulfone (PES)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
- PA6 Polyamide 6
- Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
- Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
- Silicone
- Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
- PC-PBT
- Teflon (PTFE)
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
- Polyetherimide (PEI)
- Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO)
- Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU)
- Butadiene-styrene (BS)
Injection Molding Capabilities
| Capability | Details |
|---|---|
| MOQ | Small batch |
| Delivery Time | Fastest 1 weeks |
| Certifications | ISO9001, ISO14001, IATF16949 |
| Injection Molding Machine |
|
| Die Casting Machine |
|
| CNC Machine |
|
| Liquid Silicone Molding Machine |
|
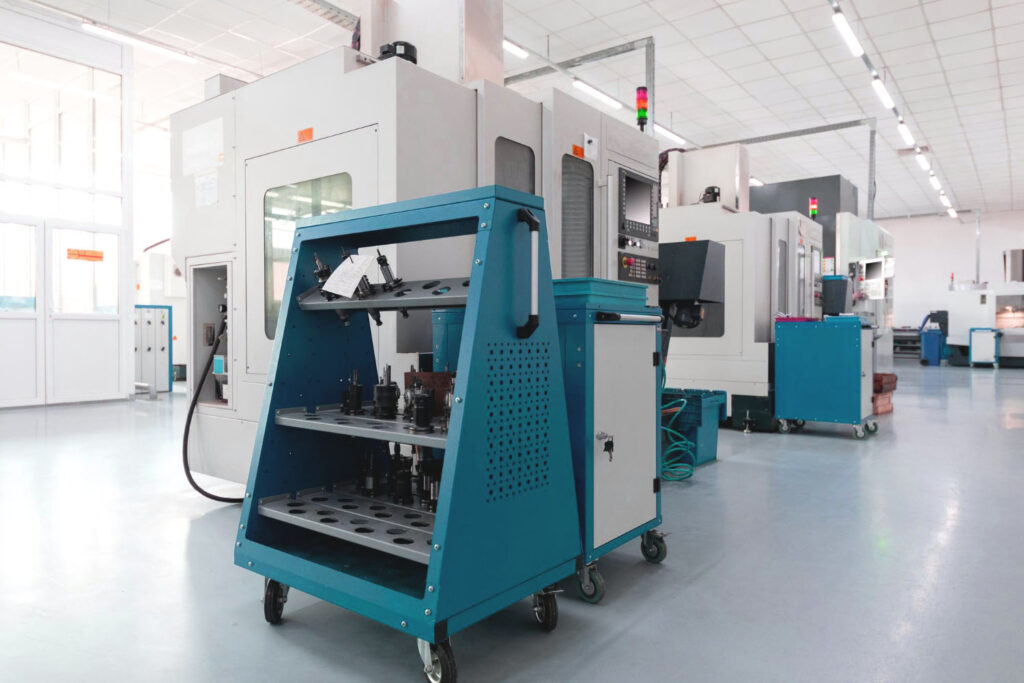

With our robust injection molding equipment and skilled technical personnel, your components will be precisely processed and manufactured. Our injection molding capabilities ensure accuracy and efficiency throughout the production process, delivering high-quality parts to meet your specifications.
Advantages of Our Injection Molding
Injection molding offers numerous advantages. For instance, its extremely small tolerances enable the easy design of intricate and precise components, while lightweight materials significantly reduce the weight of the parts.
High Quality
Efficiently
High Precision
BPA-free
Complex Parts
Cost-saving
ISO Certificate
Unlimited Size
Injection Molding Applications
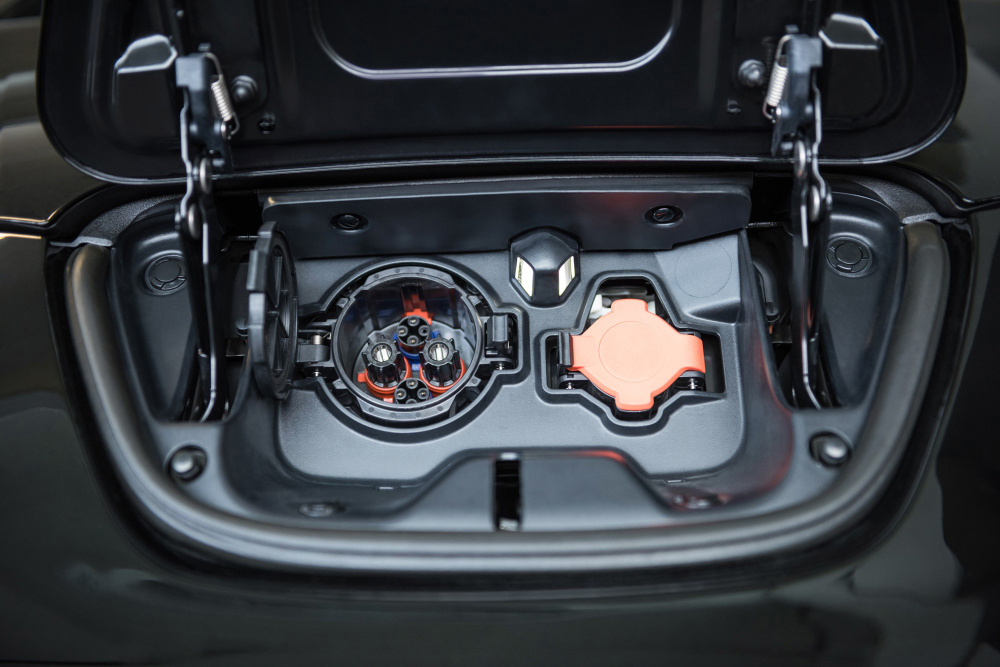
Automotive
- Dashboards - Bumpers - Body panels - Door panels - Trim components (interior and exterior) - Grilles - HVAC vents - Engine covers - Wheel arch liners - Underbody shields - Lighting components (headlamp housings, taillight lenses) - Airbag covers - Armrests - Cup holders - Center console components - Battery enclosures - Fuel tank components - Exterior mirror housings - Roof racks - Mud flaps

Food Industry
- Water cups - Drink bottles - Trays - Containers - Lids - Utensils (forks, spoons, knives) - Food packaging components (caps, closures) - Dispensing equipment parts - Food processing machinery components - Customized molds for specialty food products

Electronic
- Circuit board components (enclosures, holders, connectors) - Keyboards (keycaps, keyframes) - Mice (housing, buttons) - Laptop and Tablet cases - Smartphone cases and covers - Wearable device components (watch bands, fitness tracker casings) - Audio equipment components (speaker housings, control knobs) - Camera components (lens caps, camera bodies)
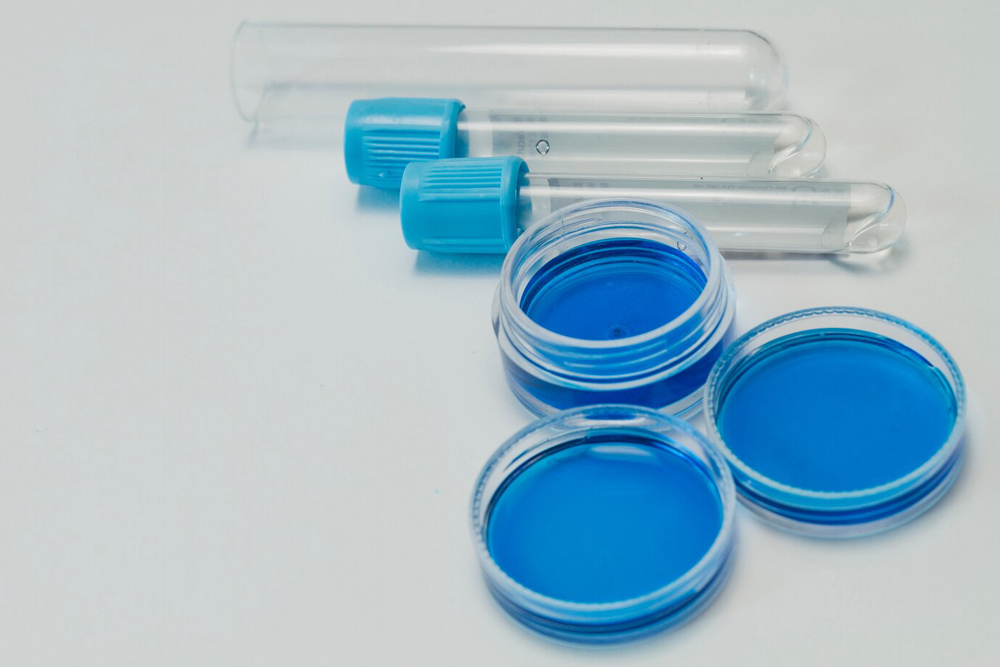
Medical
- Medicine jars and bottles (for pills, capsules, liquids) - IV catheters and connectors - Syringes (barrels, plungers, caps) - Orthopedic implants and prosthetics - Respiratory masks and ventilator components - Blood collection tubes and vials - Specimen containers (urine cups, stool containers) - Wound care products (bandage clips, wound dressings) - Medical imaging equipment parts (MRI, CT, X-ray) - Laboratory consumables (pipette tips, microplates)

Robotics
- Robot frames and casings - Grippers and end-effectors - Joint covers and protective shields - Sensor housings and mounts - Encoders and feedback devices - Motor mounts and brackets - Control panels and interface panels - Display bezels and covers - Battery enclosures and holders - Camera housings and mounts - Armature components for robotic arms - Electrical connectors and terminals - Base plates and mounting brackets

Building Industry
- Window and door frames - Siding and cladding panels - Gutters and downspouts - Roofing components (vent covers, flashing) - Insulation panels and blocks - Drainage systems (grates, channel covers) - Wall anchors and fasteners - Concrete formwork accessories (pins, stakes) - Fence and railing components - Playground equipment components - Landscape edging and borders
Injection Molding FAQs
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It’s commonly used for mass production of plastic parts with high precision and complexity.
Some limitations include high initial tooling costs, limitations in part size and thickness, and the need for careful design considerations to avoid defects like warping or sink marks.
Factors such as part complexity, material selection, mold design, production volume, and surface finishes all impact the cost of Injection Molding.
Lead times can vary depending on factors like part complexity, production volume, material availability, and supplier capabilities. Generally, lead times range from few days to a few weeks .
Design for manufacturability principles, such as minimizing undercuts, maintaining uniform wall thickness, and adding appropriate draft angles, can help optimize designs for Injection Molding.
Quality control measures include process monitoring, part inspection, adherence to standards, and continuous improvement.
Yes, Injection Molding can accommodate custom colors and finishes.
It depends on the specific Injection Molding equipment and capabilities.
Injection Molding offers high precision, fast production, and cost-effectiveness compared to other processes like machining or casting.
Emerging trends in Injection Molding technology include additive manufacturing integration, advanced materials development, and digitalization of production processes.

